1. Introduction
There are many types of castles around the world, but Japanese castles have particularly unique features. Compared to Western castles, their shape, materials, and purpose are quite different. So why did Japanese castles develop in such a distinct way? In this article, we will explore the characteristics of Japanese castles and how they differ from those in other countries.
2. Fundamental Differences Between Japanese and Western Castles


(1) Differences in Purpose
• Japanese Castles: While they served as defensive structures, they were also built to symbolize the power of feudal lords (daimyō). During the Sengoku period (Warring States period), they were important military bases, but in the Edo period, they became political centers.
• Western Castles: Primarily functioned as fortresses to protect against enemy invasions. Many were also used as residences for knights or kings, and often included villages and churches within their walls.
(2) Differences in Location
• Japanese Castles: Often built on mountains (mountain castles) or in plains (flatland castles). Mountain castles had strong defensive advantages, while flatland castles were built in key transportation hubs.
• Western Castles: Frequently built along rivers or on hills, often surrounded by moats for additional protection.
3. Unique Features of Japanese Castles
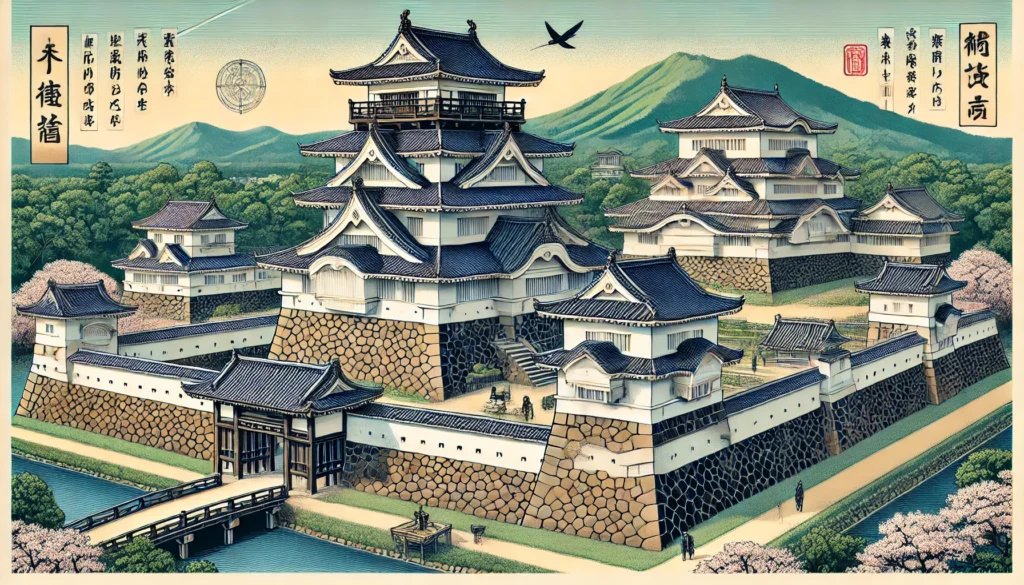

(1) The Tenshukaku (Castle Tower)
• Japanese castles feature a tenshukaku (keep), a tall multi-story structure. Unlike Western castles, this was not primarily for defense but served as a symbol of power and authority.
• Famous Tenshukaku Castles: Himeji Castle, Osaka Castle, Matsumoto Castle.
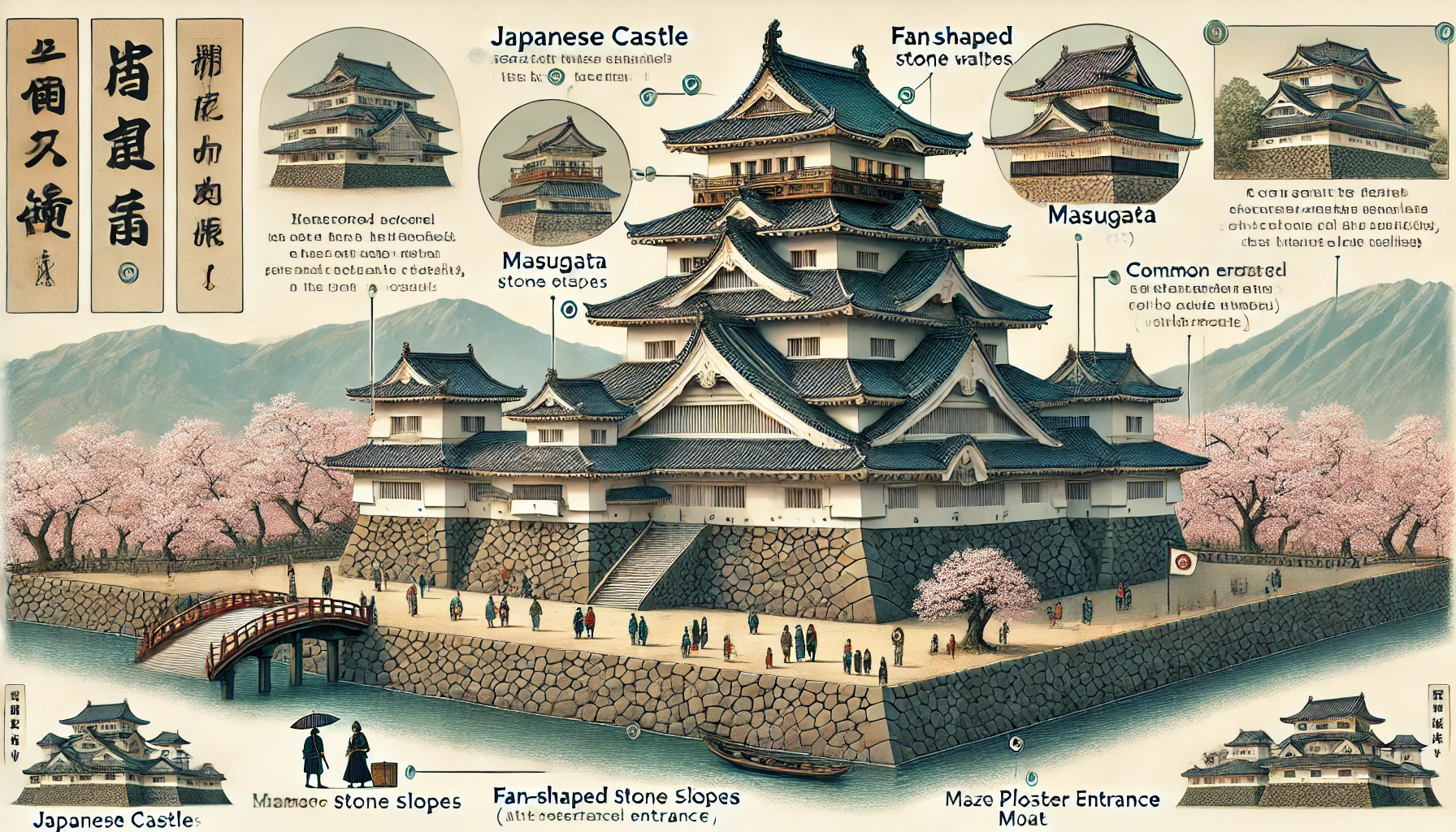
(2) Stone Walls and White Plaster Walls
• Japanese castles used highly developed stone wall techniques. A particularly famous style is the “fan-shaped slope” (ōgi-no-kōbai), which makes climbing difficult.
• The walls are coated with white plaster (shikkui), which helps protect against fire.
(3) Wooden Construction
• Japanese castles are mostly made of wood. While Western castles are built from stone for durability, Japanese castles needed to withstand frequent earthquakes, making wooden structures more suitable.
• The beauty of wooden construction is one of the highlights of Japanese castle architecture.
(4) Maze-like Layout
• The entrances and pathways of Japanese castles are designed in a complex way to make them difficult to attack.
• One notable feature is the “masugata”, a square-shaped defensive space at the gates that slows down enemy advances.
4. Why Did Japanese Castles Develop This Way?

(1) Influence of Japanese Warfare
• Unlike Western castles, which had to defend against siege weapons like catapults, Japanese castles were built mainly for siege warfare (rōjōsen), where defenders would hold out inside for extended periods.
• The layout of Japanese castles allowed defenders to survive long sieges by ensuring a stable supply of food and water.
(2) Adaptation to Earthquakes and Fires
• Japan experiences frequent earthquakes, so wooden structures were preferred over stone buildings, which could collapse.
• Since fires were a major risk, Japanese castles used tiled roofs and plaster walls to reduce flammability.
(3) Influence of the Peaceful Edo Period
• During the Edo period (1603-1868), wars became rare, and castles shifted from military use to political and administrative centers.
• The appearance and design of castles became more focused on aesthetics and demonstrating authority rather than military strength.
5. Must-Visit Japanese Castles
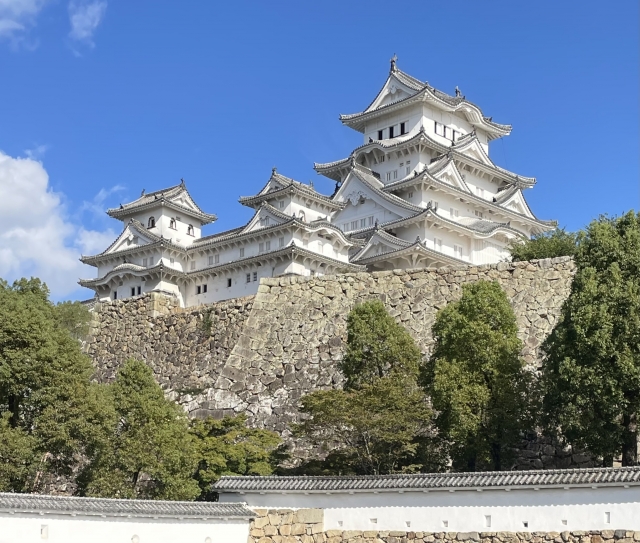

• Himeji Castle: A UNESCO World Heritage Site, often called the most beautiful castle in Japan. Also known as “Shirasagijō” (White Heron Castle) due to its elegant white walls.
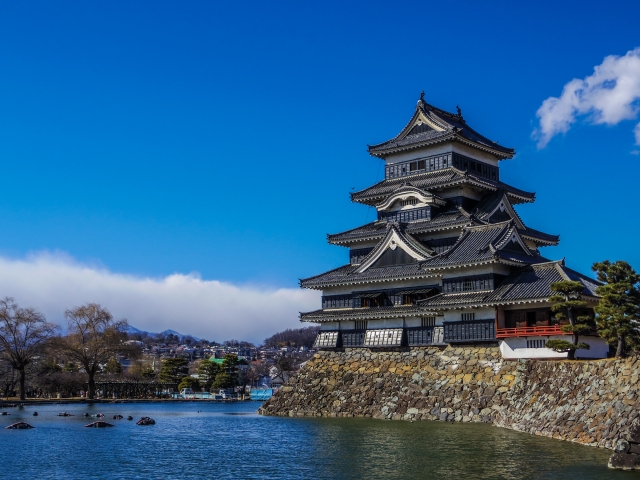

• Matsumoto Castle: Famous for its striking black exterior, earning it the nickname “Karasu-jō” (Crow Castle).
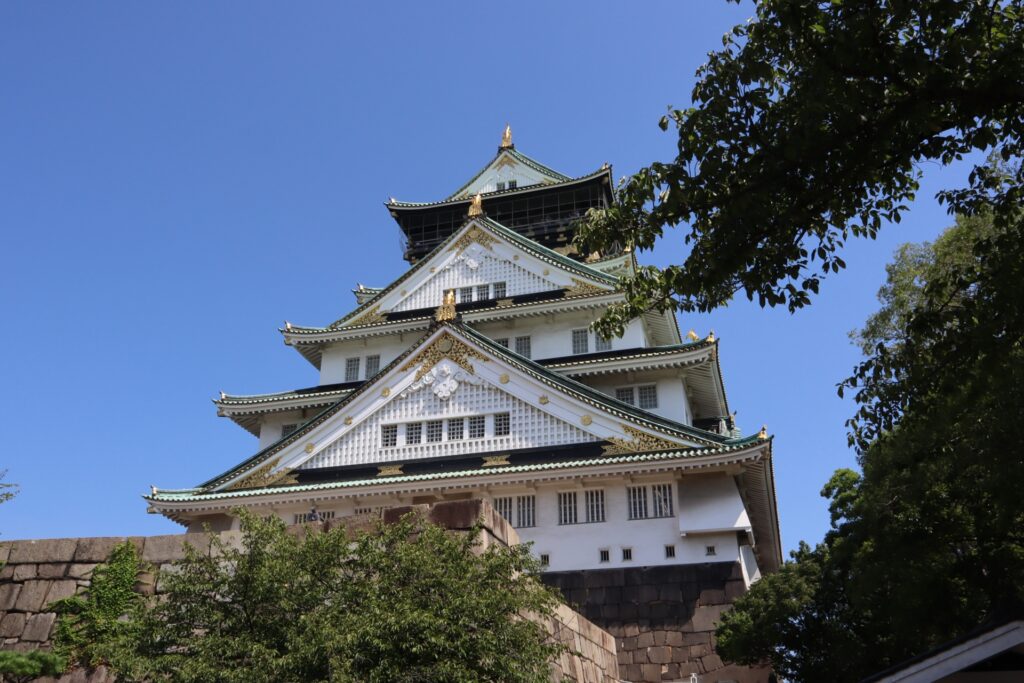

• Osaka Castle: Built by the famous warlord Toyotomi Hideyoshi, this castle played a crucial role in Japanese history.
6. Conclusion
Japanese castles evolved differently from Western castles due to unique military strategies, natural disasters, and historical shifts. Rather than being purely defensive structures, they also served as symbols of power and governance. Their elegant design, wooden construction, and strategic layouts make them fascinating landmarks.
If you’re interested in Japanese castles, be sure to visit one in person and experience their beauty and historical significance firsthand!



Comments